Hundreds of brilliant founders are now working on products that are doomed to fail. Their software ideas are too ambitious for their budget, too complex to execute, or simply have no market to capture. Yet, you don’t have to follow in their footsteps.
Over 14 years in custom software development, we’ve seen so many different ideas that had little chance of success. To help young entrepreneurs, we created a step-by-step guide to coming up viable software ideas and validating them in real-world conditions as quickly as possible.
All steps are actionable and can be executed here and now. By the end of the article, you will have enough knowledge to generate software ideas or improve the ones you already have.
Without further ado, let’s go!
Step 1. Focus on a real problem or need
In most cases, the idea is a solution to solve a specific problem or need.
Assuming this, you should zero in on defining such problems.
You don’t have to bustle the solutions right now – do not run before you can walk 😉
A problem well stated is a problem half solved.
So, look around and try to sketch out people problems or needs off the top of your head. Here are the “sources” you can also use:
- Personal problems and needs, which you are facing or may be faced with. The history shows that most successful startups and software appeared out of personal needs when a person got tired of dealing with the same problem, found nothing to solve it, and created the solution to it.
- External problems and needs refer to our environment. Direct your attention to the Outworld, define the problems of the people around you.
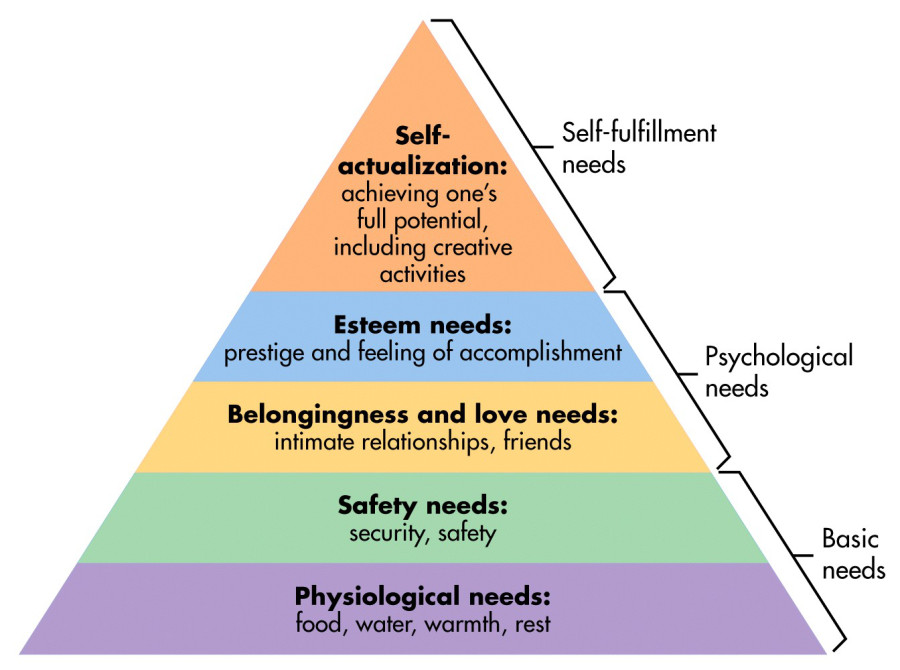
- Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, which classifies the urgency of needs judging by their importance to survival and happiness.
Source: Simplypsychology. org
Needs always exist regardless of what we think we desire. That is why this hierarchy will always remain relevant for generating mobile or web app ideas.
For example, Facebook, Twitter, Instagram are addressing human psychological needs, as each of us requires friends, relationships, an exchange of thoughts and feelings. But for people who are starving or seriously injured it doesn’t matter if someone unfollowed them on Facebook.
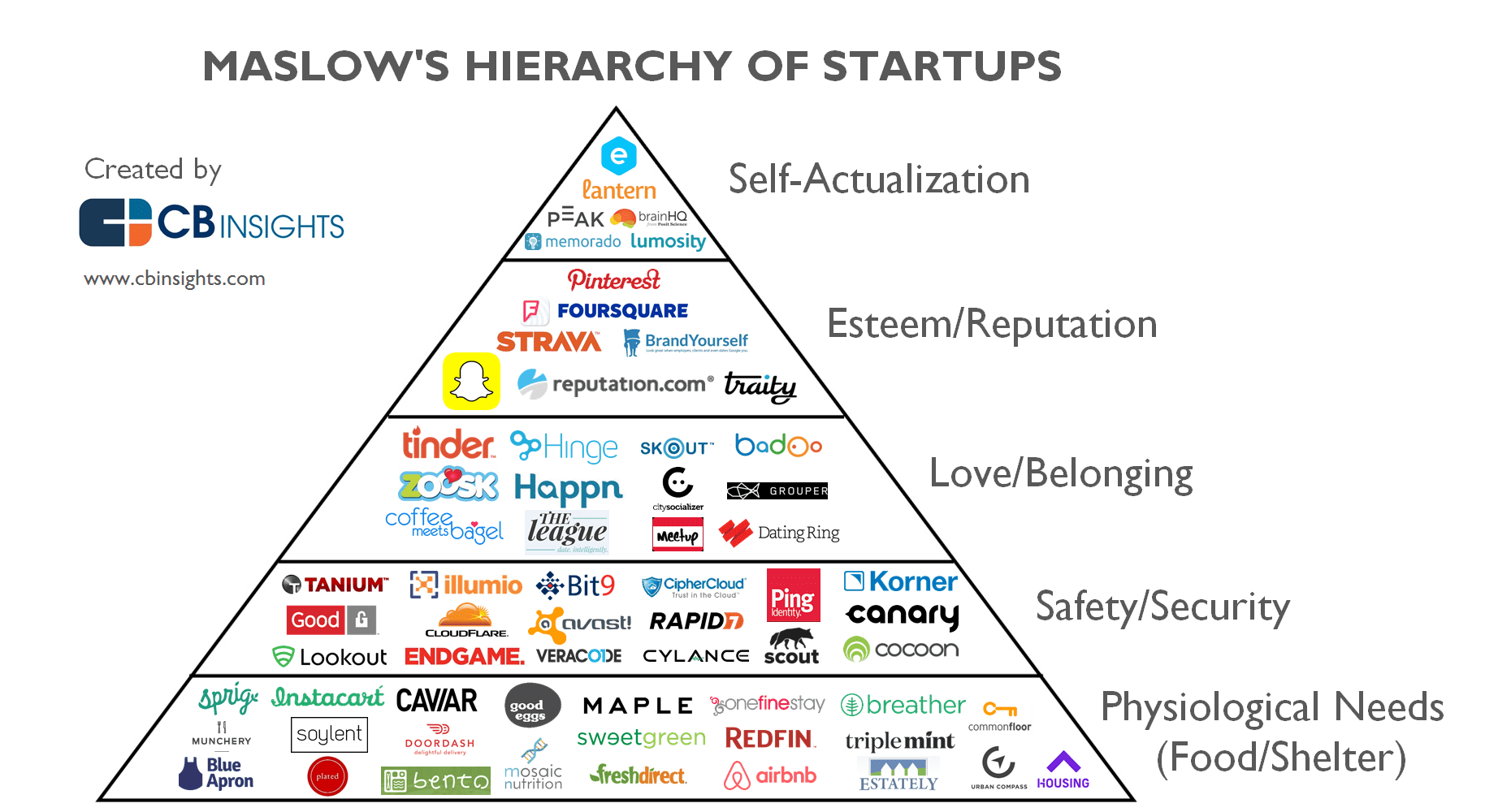
Basically, almost each software startup covers certain human needs, just look at the picture by CBInsights:
Use the above mentioned “sources” to define a list of needs and problems you would love to solve. Then ask yourself (or somebody you trust), are you (or they) ready to pay for any solution to any of the problems here and now?
If the answer is YES – write those problems down for the next step.
If the answer is NO – go on until you come across problems worth solving.
The best startup ideas are born when people problems/needs are significant and urgent, and those people cannot find an available solution.
When the problem is too painful and people are long over of trying to find a solution, you may have discovered something big.
Step 2. Qualify each problem from the list
When your list of problems is completed, you are ready to qualify the content.
To do this, we recommend you to apply the 4Us approach proposed by Michael Skok, a writer for Forbes and the founder of the Startup Secrets. It offers to answer whether your particular problem is unworkable, unavoidable, urgent and underserved?
Unworkable problems are those the customers try to solve, spend too much time and get frustrated. Most ‘workable’ problems can become unworkable under certain conditions. For example, entrepreneurs that started using MS Excel for bookkeeping and found out it to be very time consuming when their business grows.
Unavoidable problems customers can’t change but accept. Imagine you are a blogger and the government introduces a license for starting blogs. You either get one or are forced to give up.
Unavoidable problems offer the best business opportunities since people can’t resist their negative impact.
Urgent problems require timed solutions. Even if they aren’t the best, people will accept those solutions because of their urgent nature. Due to the coronavirus pandemic such spheres as online shopping, video conferencing, health care, food delivery and media and entertainment are booming.
Underserved problems are the ones which have no apparent solution, usually described by remarks like “I just failed to find a better way” or “there should be a better option”. It is quite easy to find problems and they typically hold fair business opportunities.
Take each problem from your list and ask yourself whether it is unworkable, unavoidable, urgent and/or underserved?
Now cross off those problems, which have 4 ‘NO’s.
If you find yourself answering a definitive yes to the majority of these questions, then you are on the right path toward a compelling value proposition. If not, consider revising your ideas.
Remember that it’s not necessary to solve several problems at once. Twitter, for instance, works with one main need (to stay social), which was only underserved (there was no other way to get news from around the globe so laconic and fast).
Step 3. List out possible solutions
Now change your focus from the problems to solutions.
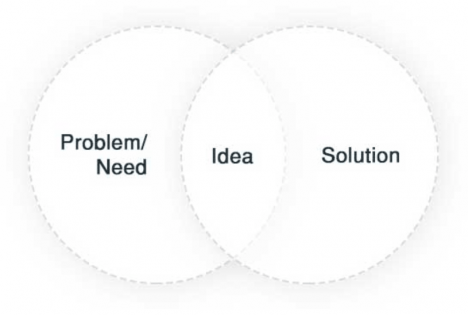
Actually there are solutions for most of the problems and this is where ideas step in the ring. Ideas are born when we match problems with solutions.
Now retrieve a match.
Note that it is hard to come up with a great solution to a problem without research. Solving your personal needs requires fewer investigations as you can provide most of the data and rely on your preferences.
You can also look for similar solutions in the market (but don’t go to pieces in case you find several competitors), try out alternative solutions (problems can be solved in a unique and indirect way), and/or interview people who are facing the problems you are eager to solve.
Step 4. Narrow down
At this point, you should have finished your list of problems and software project ideas. So, narrow down the list by asking yourself whether there is something innovative and compelling about each of your ideas.
Please, don’t get very critical about the ideas.
Sure it is quite challenging to compete with large and well-established companies, but innovations may become an excellent option to hit it big.
Even if you don’t find innovative nature in your ideas, don’t take it hard.
In most cases, startups don’t need to reinvent the wheel.
It means that you can create a successful software without implementing innovations.
Think of replicating, repurposing, or upgrading existing solutions.
Replication approach allows you to take existing model and introduce it to new market conditions. For example, Zalando was initially started as a Zappos clone and then expanded from shoes to general fashion.
Within the re-purpose concept you take an existing model and adapt it to new solutions. Just look at DogVacay, so-called Airbnb for dogs!
Upgrading the solutions is another option when generating your tech startup idea. It is usually done through building a better solution possessing higher speed and performance, and/or offering new, useful features. You might as well turn a feature of some application into a standalone product.
Step 5. Get feedback and dive deeper
The importance of getting feedback is gigantic.
Take your list and share your thoughts with a community that might be interested in your solution, you can even make a survey.
The process of discussing the idea can clarify it’s sense and even present it in a fresh new way.
Stay cool-headed as criticism is essential as it allows you to make your solution more valuable.
Most people don’t want to share the software idea with other as they think others will steal it.
Well, it’s possible but unlikely. Very few people have enough time, energy, and knowledge to implement your idea for software.
Step 6. Сome to a decision
Have you ever heard the term “kill your darlings”? This term comes from writing and means the need to remove any element which does not serve the story, even if you love it.
Do the same with your final software development ideas list. Decide what is worth the pain, and what is not. Give yourself alone time to do a spot of thinking.
Your next step on carving the perfect software idea is proceeding to market validation. Simply put, you need to understand whether people would pay for it.
If people don’t want to pay for it, they likely are not as interested in the product as they may say, or competitors are offering the same solution cheaper or for free.
Further reading: What comes after generating a software idea [Guide to market validation]
If you finish all the steps and feel right about one of your ideas, then go for it. I recommend you to read the steps at least twice to really connect the dots.
If you strive to build a million-dollar solution, try to solve a million-dollar problem or the problem one million people are willing to pay for.
If you’ve found a software idea and are ready to move forward with development, just drop us a line.
Here in MindK we have over 13 years of experience in custom application development for individuals, startups, and large companies. We would love to help you bring your software dreams to life. So feel free to drop us a line.