SPA vs MPA: what is better for your business? Facebook, YouTube, Twitter, GitHub, and Google services are all built as single page applications (SPAs). Yet, multipage applications (MPAs) still dominate the Internet. In this article, I’m going to objectively evaluate the two approaches as a CTO as a custom application development company, list advantages, drawbacks, and suggest the use cases.
What are single-page applications?
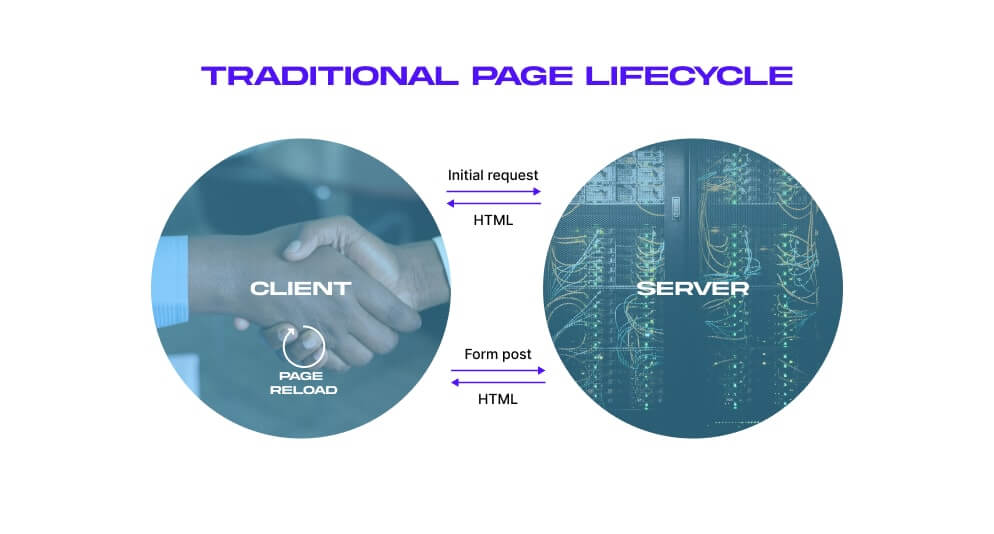
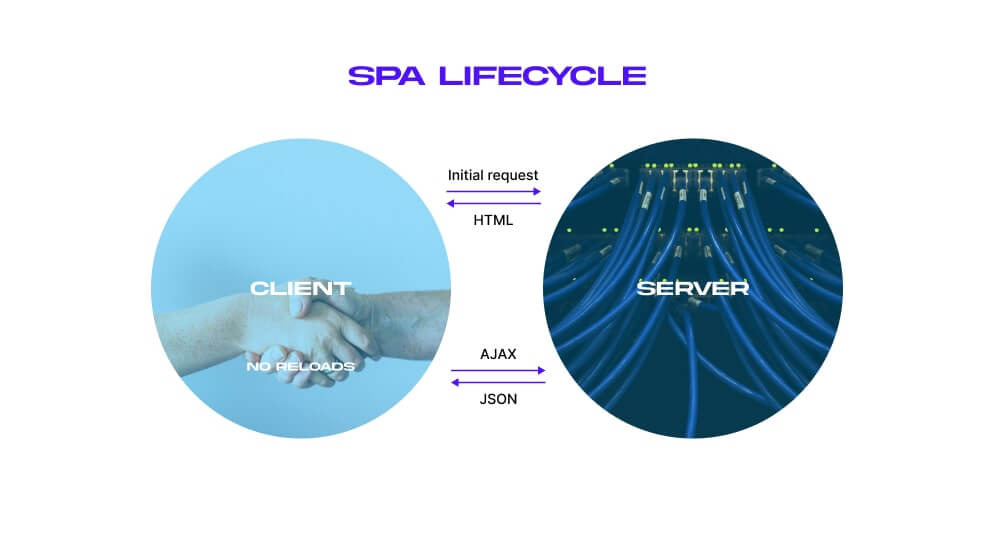
An SPA is a website that doesn’t reload when users interact with its content. Any new information is added dynamically to the page, creating an experience similar to desktop software.
Now, let’s go a bit more technical. When traditional applications react to your input or have to display some new content, they request a new HTML page from the server. After receiving the markup, the browser renders the new page causing it to reload.
AJAX (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML) allows web applications to refresh only a part of a page.
When you interact with an SPA, your browser makes an AJAX call to the server. But instead of rendering a new page, the server can just send you the data (usually in a JSON format). The SPA will then use that data to render some parts of the page directly in your browser.
The result is an application that consists of a single highly-interactive web page that never completely reloads.
So now you know the basic difference between SPA vs MPA, let’s dive deeper into their advantages and drawbacks.
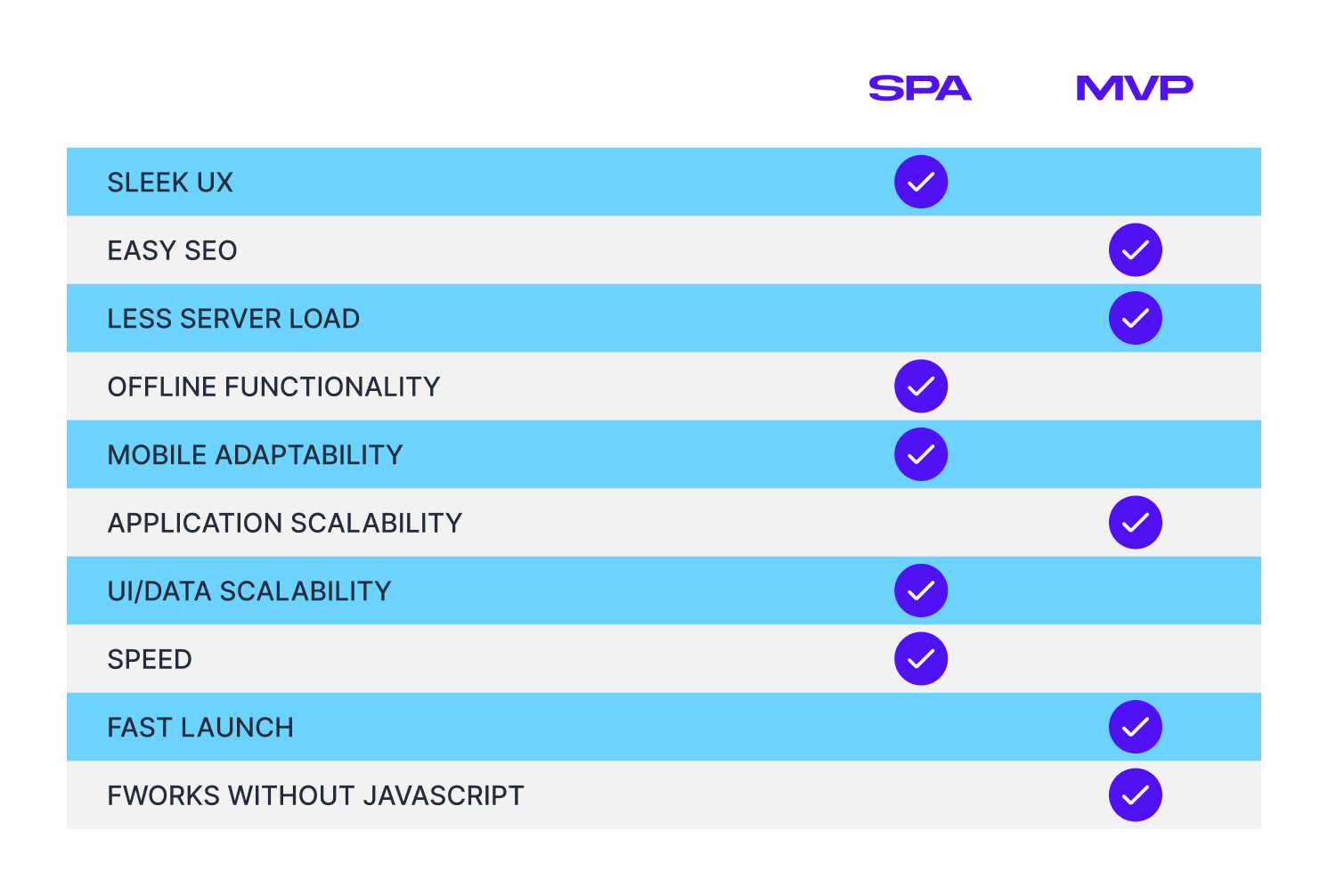
Advantages of SPA
There are seven main perks that make single page application more attractive vs multi page applications.
1. Fast and smooth UX
Constant full-page reloads hurt the user experience.
You’ll never find this problem in SPAs. JavaScript, CSS, and HTML only load once. After the initial load, the server only sends you the new data. This decreases the server-client traffic and makes the app feel “snappier”.
With the traditional applications, the server has to generate complete pages for thousands of users. But with SPAs, the rendering is done on the client-side. This means the server responds much faster to user requests.
So as long as you don’t use horribly outdated hardware, SPAs are much faster and responsive than traditional web applications.
This makes them the ideal candidate for porting old desktop apps and enterprise-grade solutions to the web without altering their UI and workflow.
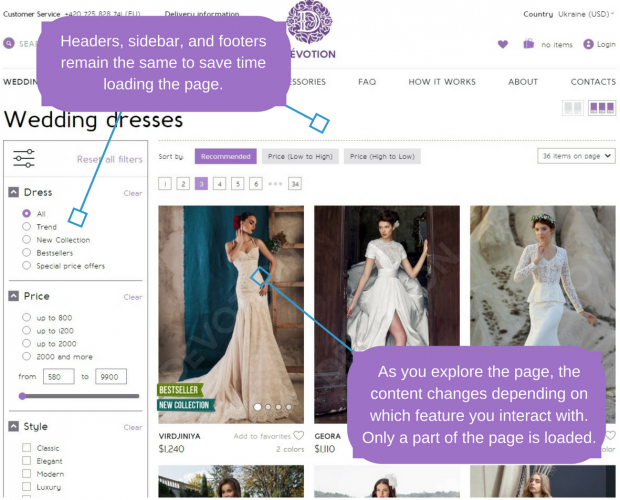
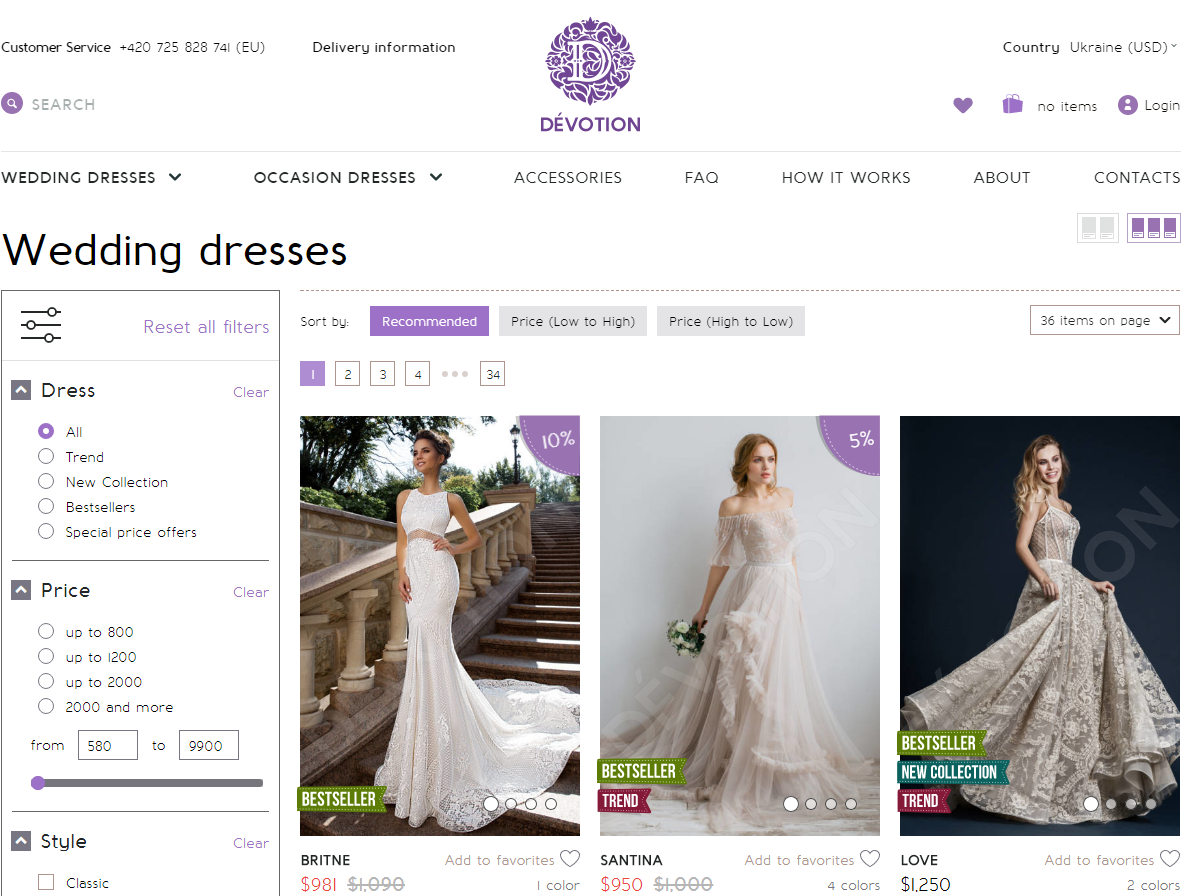
Devotiondress.com
2. Local caching and offline functionality
After the initial request, single page web apps cache all the data they receive from a server and store it locally. Therefore, SPAs can continue to function even if the Internet connection fails.
This is especially important for healthcare software development. Patients require attention, even if their Network is down. We’ve recently added an offline mode to an EMR system for lactation care. It prevents the loss of critical information during an outage and allows doctors to complete the patient’s chart without the Internet connection.
When the application connects back to the network, it synchronizes the local data with the server and restores the full functionality.
You can also partially forgo using cookies in favour of Web Storage. Although pretty similar in function (tracking users, their settings and preferences), local storage can store more data (5MB vs 4KB per cookie).
It also doesn’t have to send data back to server with each HTTP request. This speeds up the loading of static files (JavaScript, CSS, images and other media).
Custom Electronic Medical Records (EMR) system, developed by MindK as an SPA
3. Perfect Mobile Adaptability
By the end of 2017, the mobile Internet speed remains almost twice as slow as its fixed counterpart. At the same time, users are all too eager to abandon slow apps. So it should come as no surprise that mobile users would benefit the most from apps that load faster.
Moreover, single page applications are significantly easier to port from web to mobile. You can generally use the same backend code both for the web and iOS/Android versions of your app, which is quite rare with the traditional approach.
And finally, compared to MPAs, single-page UI is much closer to that of native apps. This means you won’t have to change much design wise when adapting your SPA to mobile.
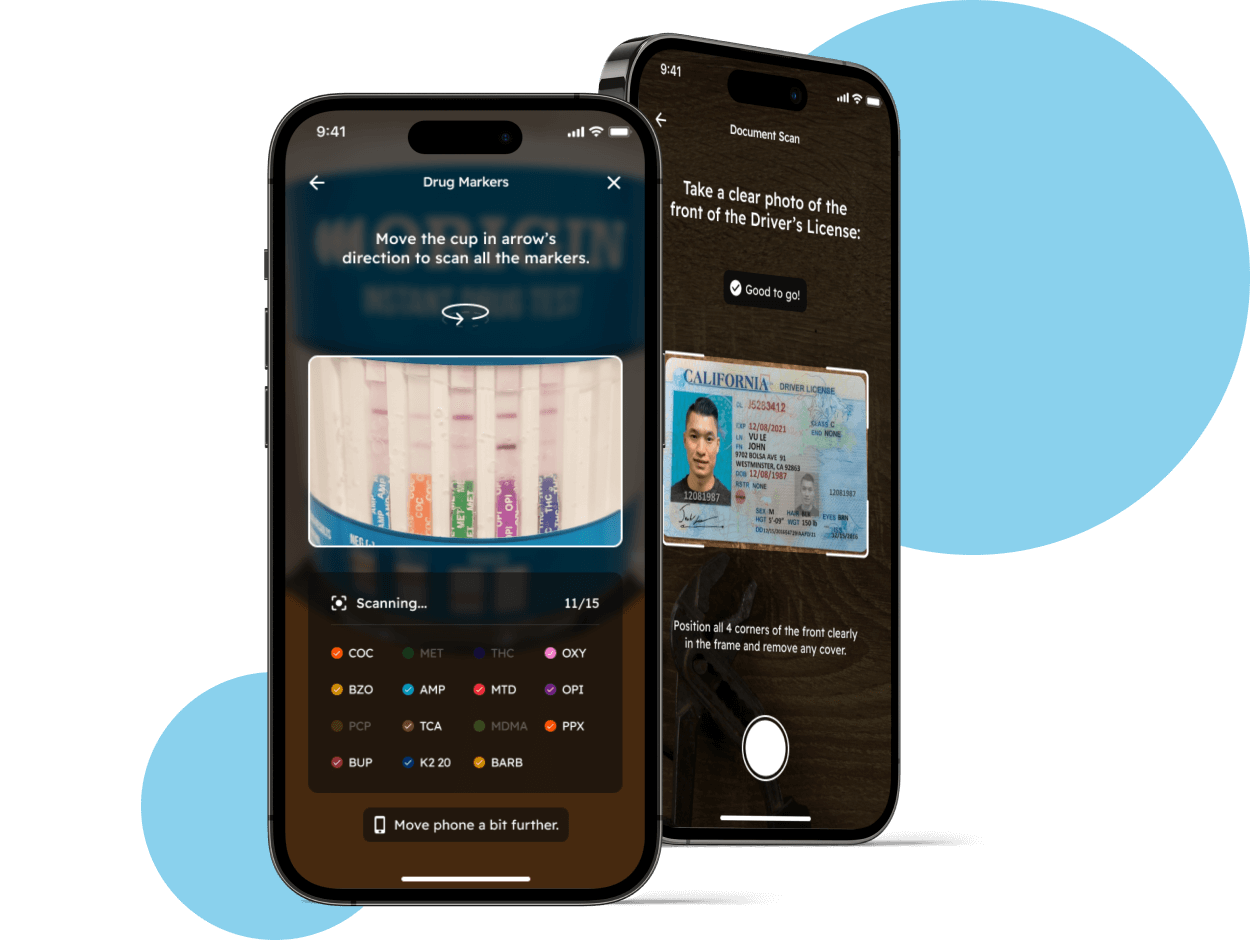
SaaS SPA that now covers 377 healthcare services started as a humble app for AI-powered drug testing.
4. API reuse to cut costs
It’s also much easier to create an SPA if you already have a mobile app. If the app communicates with some APIs on the server-side, you can likely reuse the same APIs in your web application without significantly altering them.
And visa versa, if you’re planning to launch a native app, the APIs you’ve written for your single page web application will come in handy when you start the mobile development.
5. Streamlined development
Single page application development is similar to building a house with LEGOs. Once you’ve got the components (LEGO bricks), you can quickly construct the SPA without the need to add the same code fragments over and over.
Also, you don’t have to write custom code for rendering HTML pages on a server. And it’s much easier to initiate the development from a file://URI as you don’t need a server at this stage.
Finally, SPAs are significantly easier to deploy and version in production.
6. Back-end/front-end separation
In single-page applications, UI is separated from data. This allows you to revamp your frontend and alter the UI as much as you want without affecting the backend (barring some static resource files).
Decoupling of front-end/back-end development makes it easier to find bugs in your codebase. It’s also easier to integrate new APIs and alter the ways in which data enters the SPA framework and flows to different systems. All without affecting the UI.
7. Painless Chrome debugging
It’s much easier to debug single-page applications with Chrome. You can see the whole code at once, observe the network operations and inspect page elements together with the associated data.
And don’t forget that the single page application javascript frameworks have their own Chrome DevTools extensions like Vue.js devtools, Ember Inspector, or React developer tools.
SPA Drawbacks (and how to fix them)
Let’s now look at the popular (and often misinterprited) arguments for choosing MPA vs SPA.
1. SEO issues
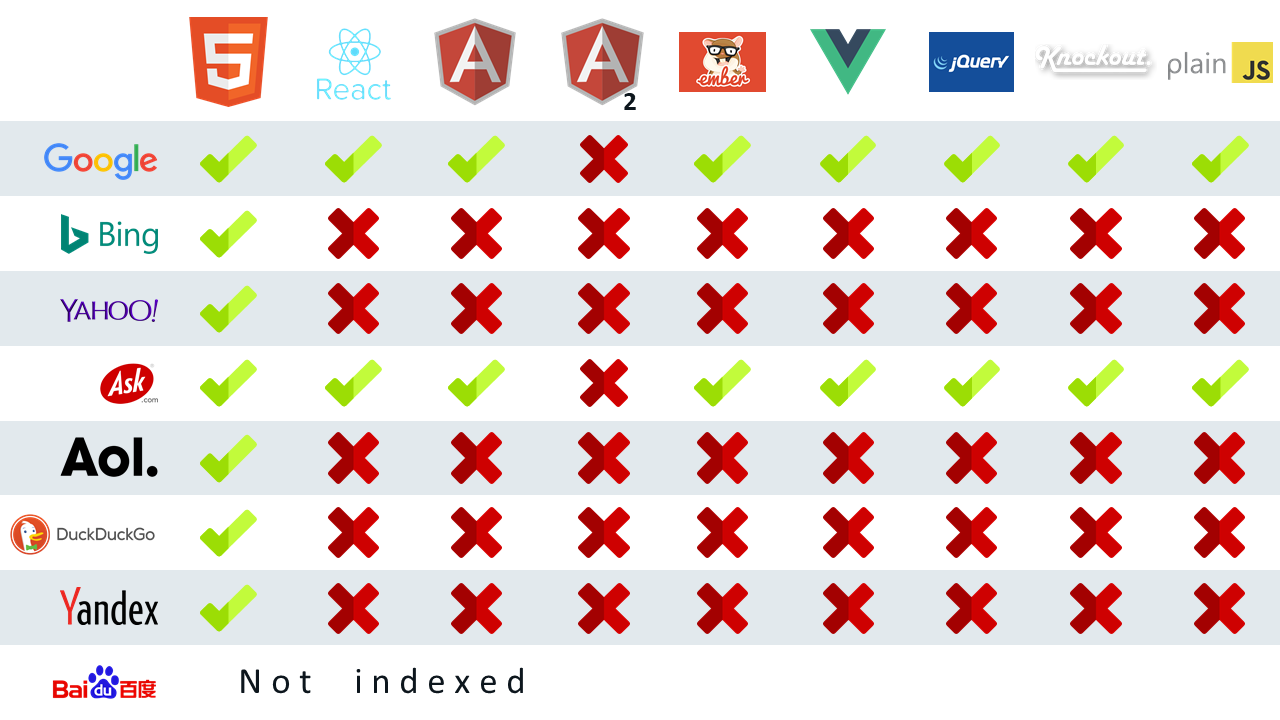
For a long time, Google and other search engines had troubles with indexing SPAs. Their bots were good at crawling static HTML pages but were ill-equipped to render the dynamic content. And without the ability to execute JavaScript, all they saw in an SPA was an empty HTML container.
In the last couple of years, Google has become much better at indexing JavaScript.
Still, Google admits it sometimes can’t properly index single-page applications. Not to mention that other search engines haven’t yet achieved the same SPA-crawling prowess.
Search engines crawling SPAs created with various JS frameworks. Source: moz.com
Another SEO issue comes from the fact that SPAs have a limited semantic kernel when compared to the traditional applications. This originates from the fact that it’s simply impossible to stuff as many keywords into a single page website.
To solve this problem, choose your content to better match the user requests. Also, take advantage of meta descriptions, tags, and internal anchor text links. Use free tools like the Attrock Meta Tag Analyzer to optimize your meta tags. Or you can dedicate your SPA to a single subject as Google gives higher rankings to thematic sites.
Finally, you may run into some shareability issues as Facebook’s bots are hilariously bad at crawling SPAs.
Further reading: How to solve the common issues with single page app SEO, set up Google Analytics, and enable rich social sharing.
2. Memory leaks
Event listeners used in SPAs can cause a loss of available memory on the user devices. Since your app is essentially a single page that never reloads, memory leaks get worse the longer SPA runs.
If you don’t pay enough attention to this problem during development, it can lead to significant slowdowns and quickly drain the device’s battery.
Further reading: how to detect and fix memory leaks in JavaScript applications.
3. Security issues
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) makes SPAs a bit more vulnerable to hacker attacks. XSS allows trespassers to insert malicious client-side scripts into otherwise trusted applications.
But there are ways to combat Cross-Site Scripting. With single-page applications, you can secure your data endpoints and separate the JS that gets downloaded by a client into multiple isolated pieces.
This way, attackers won’t be able to access all your code at once.
4. Slow first load
SPAs launch slower than the traditional applications. This happens due to client-side rendering. Before your browser can render the page, it has to load bulky JS frameworks. This could take a while, especially for the large application.
But after the first render, SPAs become much faster than MPAs.
Fortunately, there are ways to speed up the SPA initialization such as loading assets dynamically and minimizing the scripts.
5. Limited functionality with JavaScript disabled
A small percentage of users disable JavaScript in their browsers. The reasons range from increased speed to security concerns. For such people, your cutting-edge SPA would be downright unusable.
The partial solution for this problem is to use server-side rendering for the first load. Still, some of your app’s functionality may remain unavailable with the JS disabled.
Progressive enhancement philosophy also allows you to create applications that deliver a satisfying experience to people who, disable JavaScript, or use outdated browsers and hardware.
Devotiondress, an SPA that works with JS disabled
6. Poor app scalability
With the traditional approach, the application’s functionality is spread over multiple pages. You can gradually add content and expand the pagecount. It’s also relatively easy to alter a part of your MPA without affecting the other pages.
If you want, for example, to change the application’s framework, you can do it page by page until the whole MPA is redesigned.
In SPAs, the business logic is built into the separate components that are easy to develop and maintain.
But making changes to the app’s architecture is a whole other story. A single feature may consist of several components and altering a commonly used element can affect other parts of the application.
That’s why you have to take into account the future changes to the SPA’s functionality during the planning stage. If you have a clear vision of where your application is heading, the developers will be able to factor in the possible changes before the architecture is set in stone.
7. Navigation issues
In SPAs, back and forward buttons have some unexpected behavior.
Instead of returning you to the prior state of the app, the back button can actually load the previous page (which can lead you to a completely different website).
When you press the back button, the app may also lose the scroll position so you end up on a different part of the page.
In some SPAs, you can’t even open a link in a new tab, refresh a page, or bookmark it.
Fortunately, you can fix the navigation issues with HTML5 History API, which is already bundled with the majority of JS frameworks.
8. Weird behavior due to asynchronous requests
SPA manage user requests asynchronously and this can lead to some unexpected behavior.
When you press a button or click a link in a traditional application, it will stop all current activity and make a new request to the server.
But in SPAs, the server responses come asynchronously. This means they can arrive not in the same order as you’ve requested. So if you click several links really fast, you can end up on the wrong page. Or you may experience graphical glitches if you press the same button several times.
Your developers will have to write code specifically to handle such situations.
Conclusion
Before picking your side in the SPA vs MPA debate, consider your goals.
Want to offer multiple services or different categories of goods? In such a case, creating a multipage website is the logical solution. That’s why enormous applications like Amazon are built this way. MPAs are also a good idea for websites that have a lot of content (such as news portals) and require flawless SEO.
Wish provide a single service or product and need superb UX? SPAs allow you to pack impressive functionality into a lightweight application. SPAs are ideal for highly interactive applications that look great on any device.
Single-page apps are great for data-driven medical applications, ERP systems, and interactive dashboards in SaaS products. Most of our new clients at MindK end up going the SPA way.
So if you have trouble picking the right approach or need a team of engineers for your project, you can always contact us.