Location Intelligence (LI) is a $50B+ opportunity for all kinds of businesses. The niche is growing at an amazing rate of 15.6% a year. So, what exactly is Location Intelligence? And what does it have to do with location-based app development?
I’m Dmitry Ieremenko, a Senior Engineer at MindK. For the past year, I’ve been helping to build an app for real estate investors that uses location data as its main advantage. Here’s how you can benefit from Location Intelligence using the cloud-native approach. And yes, I’ll keep the language as accessible as possible;)
Table of contents:
- What is Location Intelligence (LI)?
- Location Intelligence use cases
- Examples of Location Intelligence in various industries
- Types of geospatial data to power new business capabilities
- How to bring it all together: the cloud-native approach
What is Location Intelligence (LI)?
Simply put, it is the use of GPS or mapping data to discover insights about your market and customers.
Here’s an example. Did you ever have Starbucks send you a discount on your favorite caffeinated drink when you were about to pass by one of their outlets? To achieve this, the company must track the location of your smartphone. Starbucks combines this with their CRM info – the type of coffee you like, the time you regularly make purchases, and so on.
Yet, location-based technology has a much higher potential beyond simple advertising. Boston Consulting Group (BCG) has recently run a massive survey of 500+ executives in various niches.
- 95% of respondents said Location Intelligence was critical to reaching their business goals in 2021.
- 91% think it will become even more important in 3-5 years.
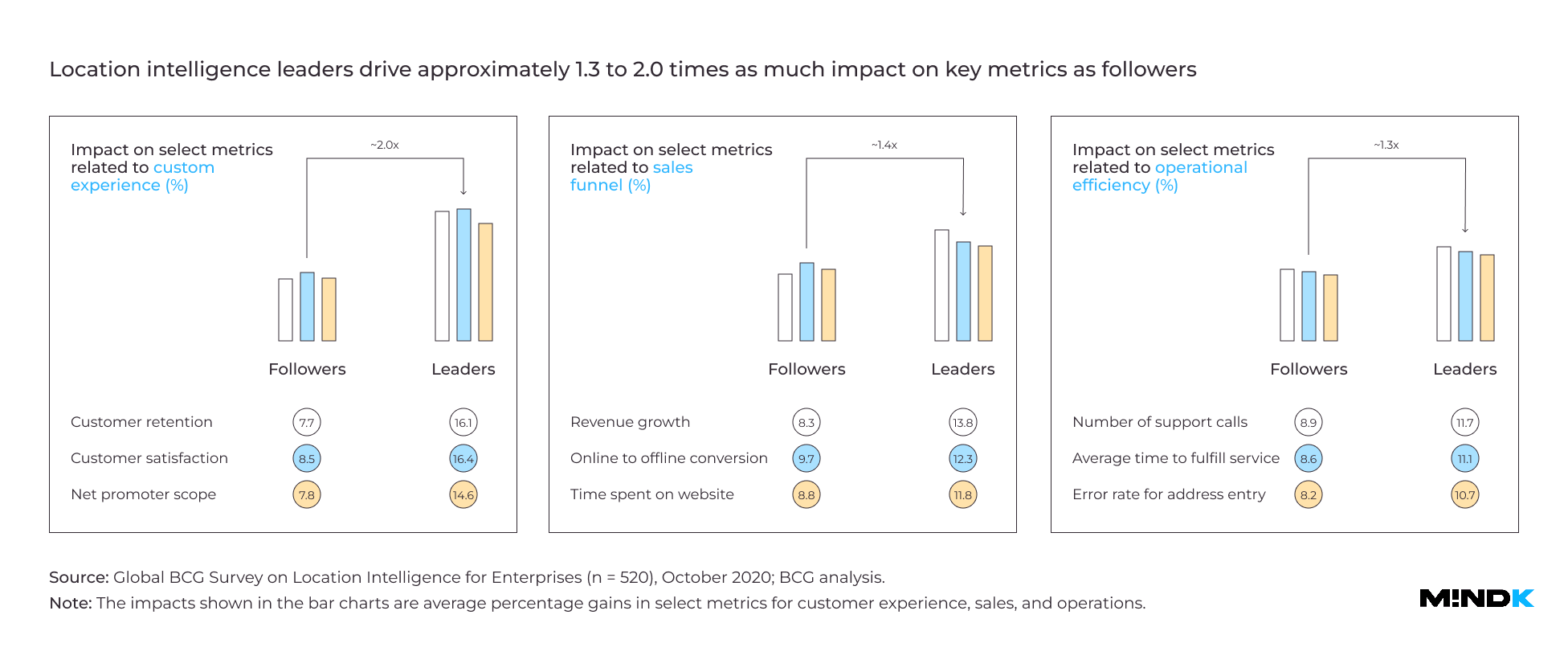
- Leaders in LI report 2x higher satisfaction rate, sales volume, and back office efficiency than competitors.
And location-based technology isn’t just for the world’s largest enterprises. Cloud-native services, state-of-art analytics, and data exchanges make it much more accessible to smaller businesses.
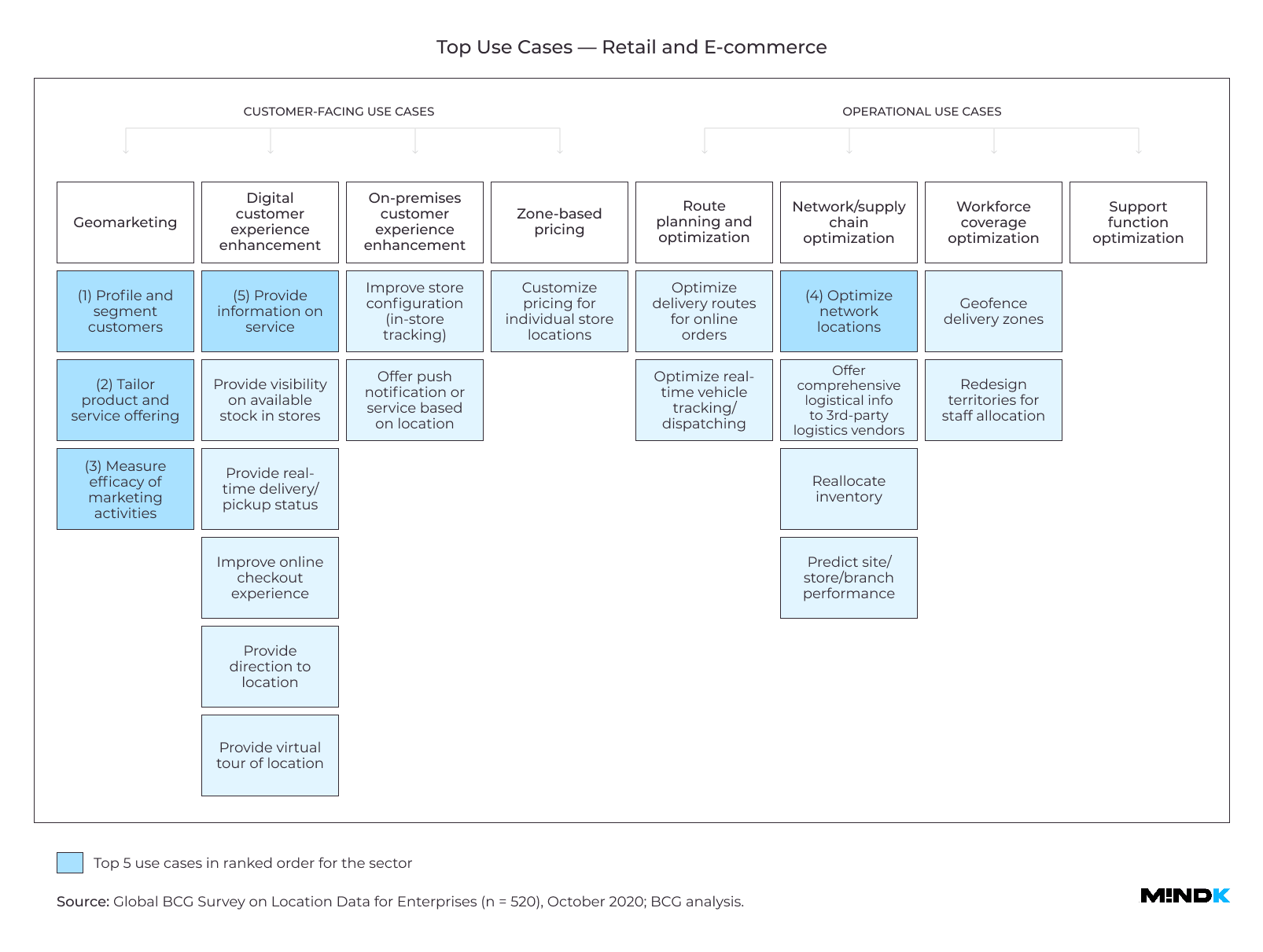
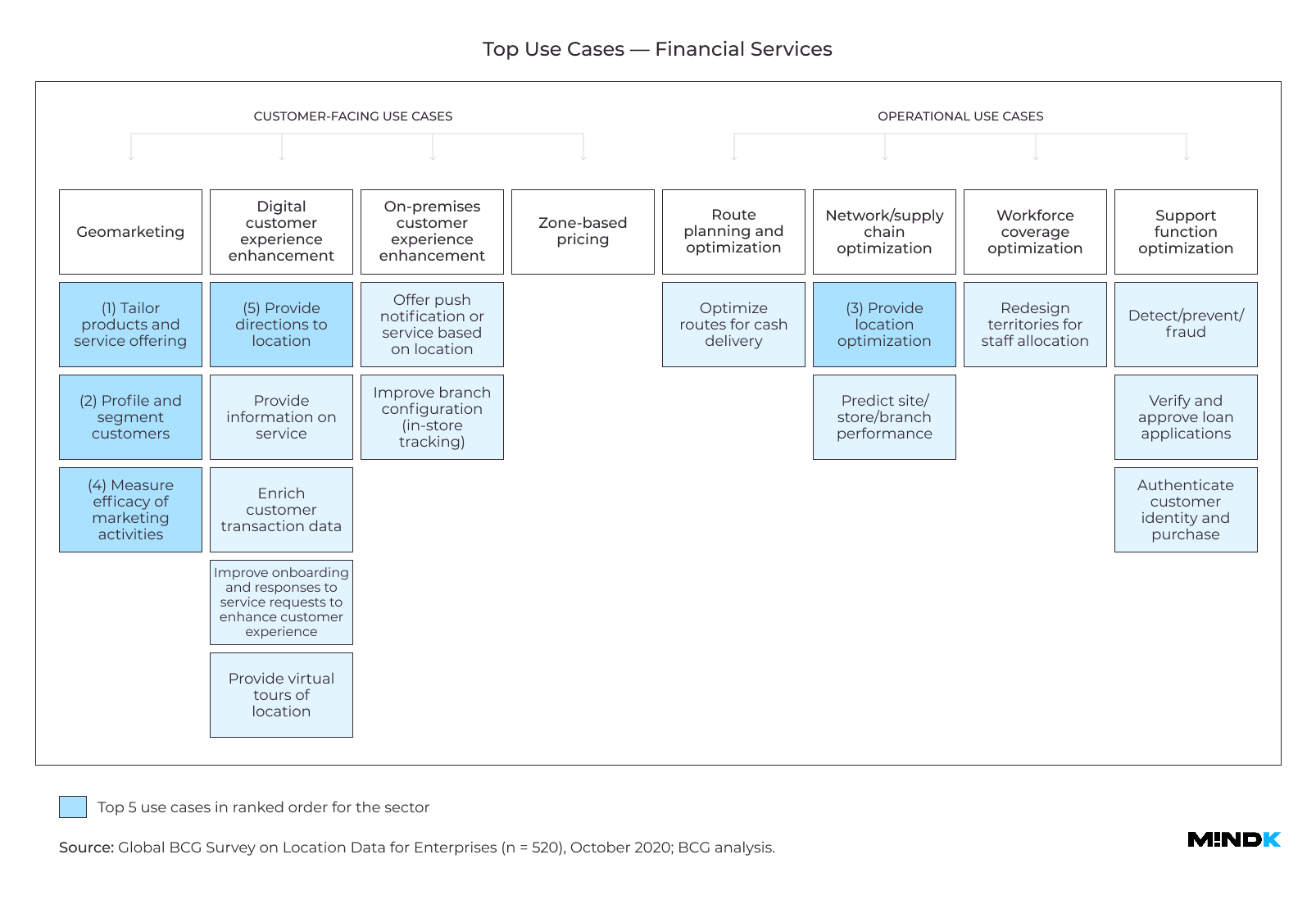
Location Intelligence use cases
Most companies struggle to provide better customer service in the face of rising competition. They also seek to optimize their business operations, cutting costs and improving profit margins. Location Intelligence can help you with both goals.
Customer-facing use cases
- Location-based marketing
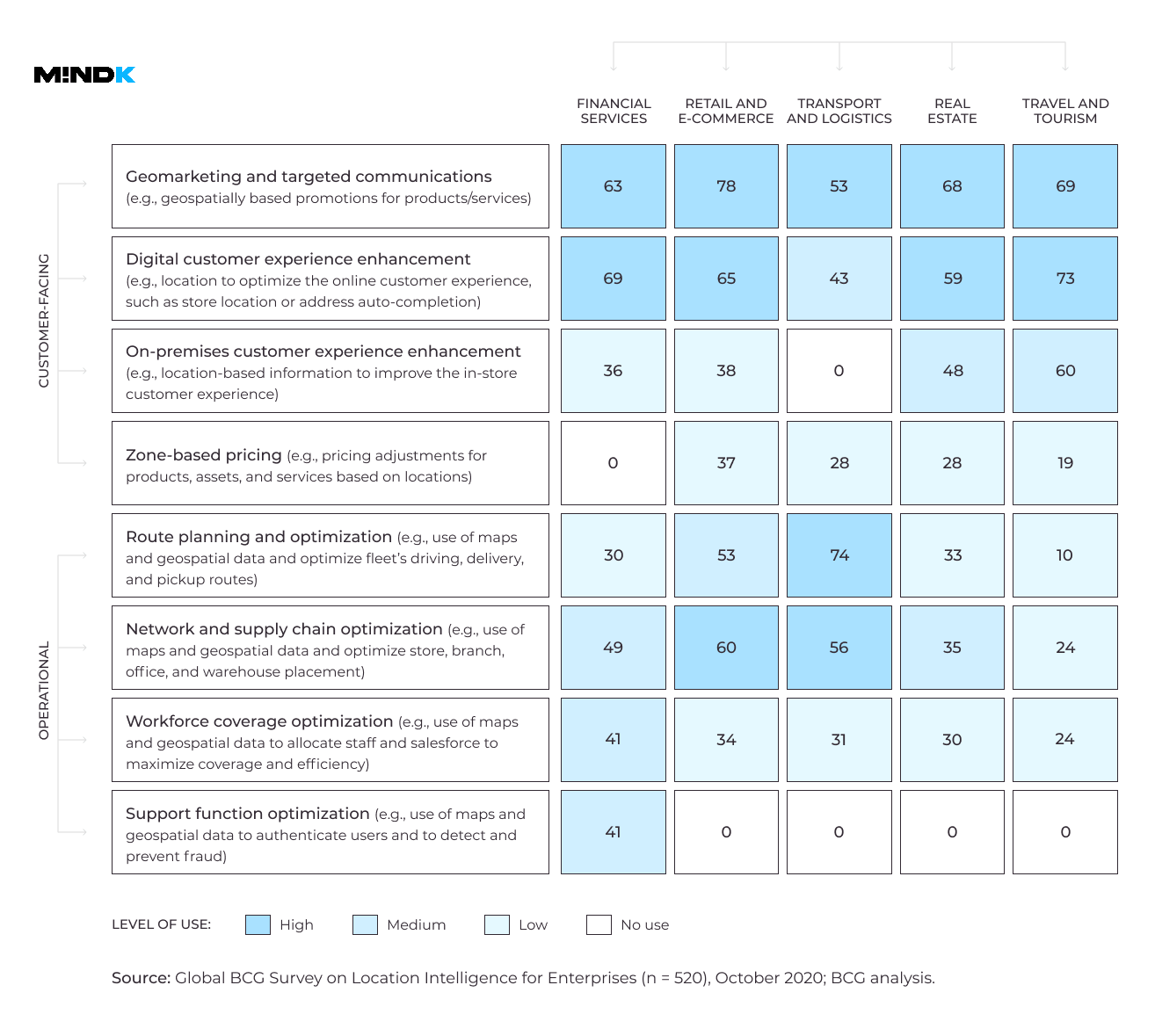
Geomarketing, or geo-push, is a staple in geolocation app development. You can combine a user’s position on a map with their shopping habits, preferences, and interests. Then, send them targeted offers at the right time. 78% of executives in the BCG study use this trick to engage customers.
- Improving digital product experience
Some of the world’s top enterprises use LI to augment search, discovery, and map functions in geolocation tracking apps. Real estate software often layers property data on top of a map interface. Yo can see commute times, property valuations, crime rates, and other important factors for selecting a home. Map-based search is now essential to real estate apps. In fact, a 1-second delay in map loading speed can lead to a 15% drop in conversions according to the BCG study.
- Improving experience in physical stores
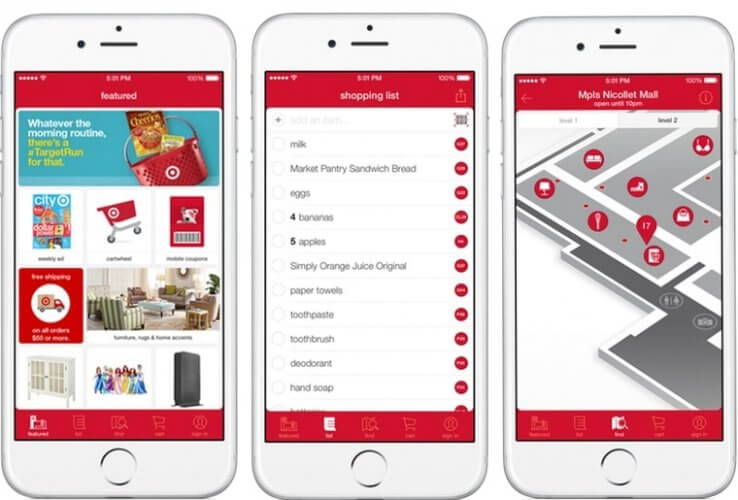
Large retailers like Walmart and Target use interactive maps to help customers find products inside a store. They can also send discount offers based on the person’s spending habits.
- Location-dependent pricing
Everybody knows that changes to price can affect the demand. For some products, this relationship is very strong. For others, the effect is almost negligible. This is called price elasticity of demand. One takeout food delivery app can adjust prices according to local differences in elasticity. According to BCG, this feature is now responsible for 25% of the company’s revenue.
Source: Target
Operations-oriented use cases
- Delivery route planning
Optimizing logistics and route planning can give massive benefits for any company that moves packages. UPS, for example, saves over $200M a year with the help of advanced network planning software. According to the BCG study, using LI to route parcels can save you up to 6% in delivery time and costs.
- Supply chain optimization, staff scheduling, and allocation
LI can help select locations for the company’s offices, ATMs, and storage facilities. Just take demographic information and foot traffic data. Then add local demand indicators – convenience stores, ATMs, and petrol stations nearby. And you can determine promising markets for expansion.
- Fraud prevention
US Bank, for example, looks at your smartphone’s location every time you pay with your card. This helps identify stolen cards and prevent declined transactions during international travel—a neat idea for geolocation app development.
Examples of location intelligence in various industries
Location Intelligence can provide tangible benefits for almost any industry. To prove this fact, here are some examples of real companies that use LI in 6 different niches.
Retail
Spencer’s Retail is a one-stop shop with over 160 locations across India. It started using Location Intelligence with a simple map that pointed customers to nearby stores. The app shows the availability of goods at different stores. It also gives advice on whether your pickup location is outside the retailer’s service areas. This has all but eliminated non-serviceable orders.
The company also switched to a digital route planning system. In 96% of cases, Spencer’s can now ship a parcel in under 4 hours, which is impressive for a country the size of India.
BCG survey shows that LI can help retailers increase the average cart size by up to 15% and decrease the last-mile delivery costs by up to 4%.
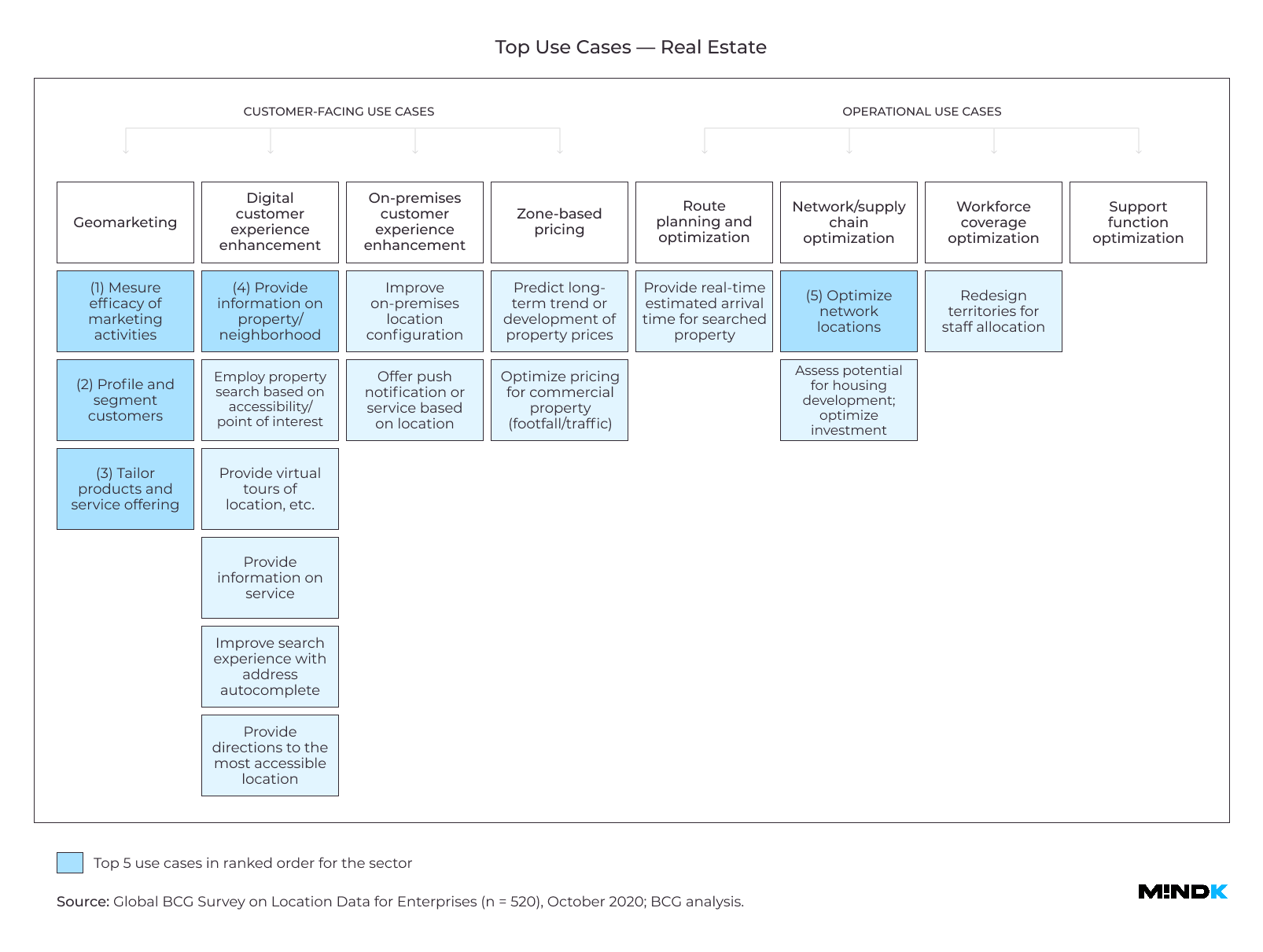
Real estate
Displaying a map for property searches once could elevate your real estate app above its rivals. Now it became a basic expectation of customers around the world.
To overcome competition, one of the American real estate pioneers started investing in more advanced use cases for Location Intelligence. It combined granular location data with CRM information to find the people most likely to convert in the near future. It also used mapping and topography data to improve the property valuation modeling. The company combined these two features in a new service – buying real estate from people needing quick money.
The company’s map now has multiple new data layers that help users find and compare different real estate options:
- Estimated commute time based on real-time traffic data.
- The ease of walking to venues nearby.
- Similar properties in the neighborhood.
- Availability of parking lots, schools, kindergartens, and other places of interest.
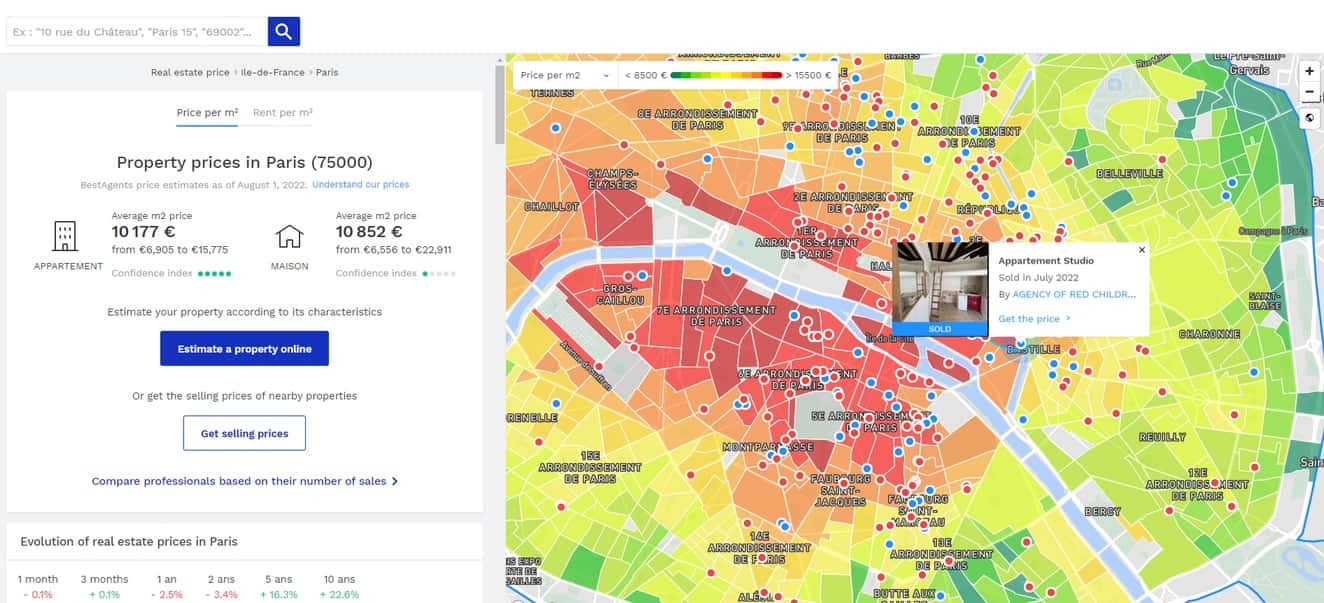
A heat map for property pricing is one of the possible use cases for Location Intelligence in real estate. Image source: meilleursagents.com
User testing showed that adding a map to real estate apps is essential to fulfilling customer expectations (even if your map is quite similar to your rivals). What’s more, introducing new types of map data can have a tangible effect on business KPIs. For example, users who had access to improved school data showed on average 10% more conversions when going from the map view to property listings.
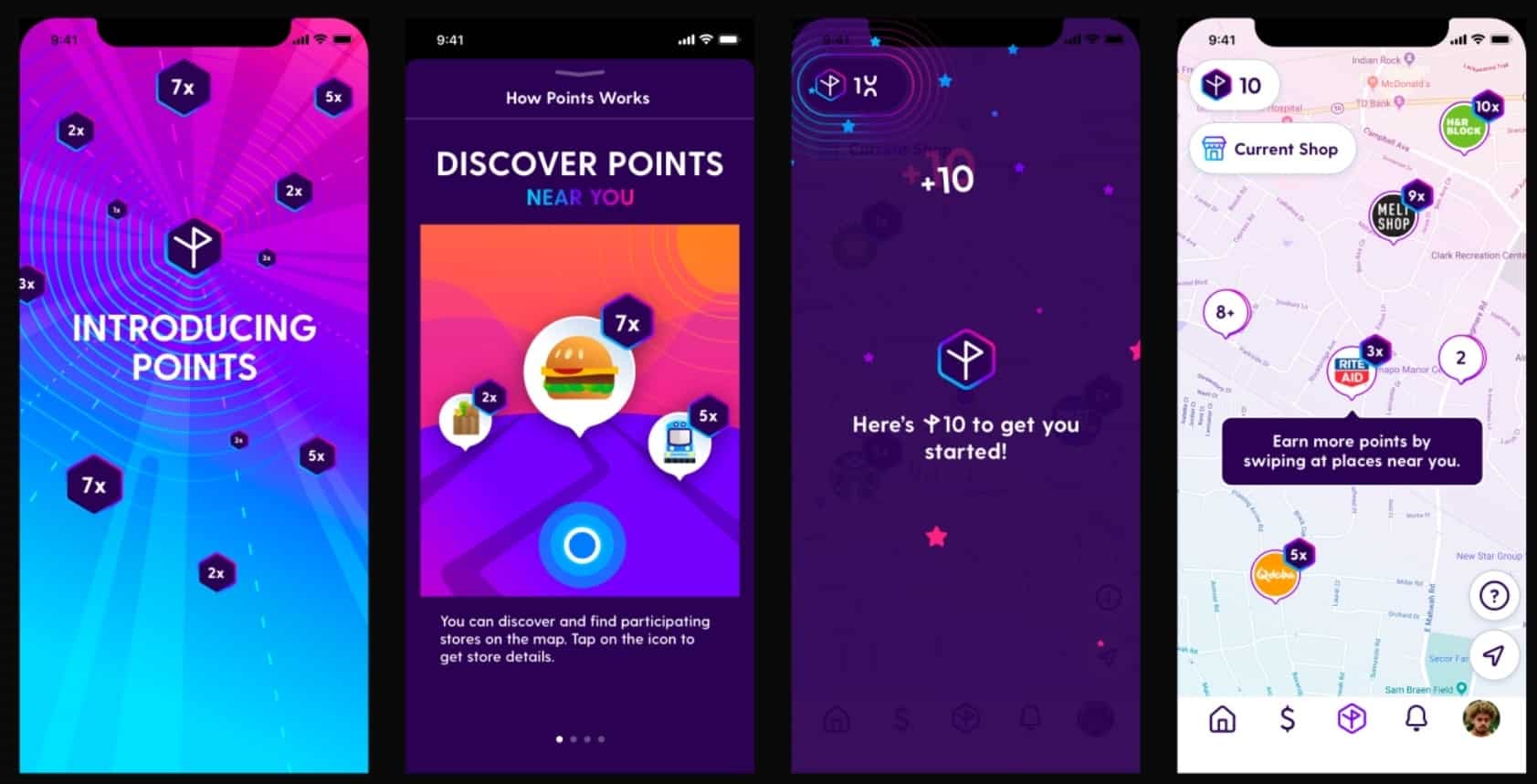
Finance
Current is a New York-based mobile bank with over $402M in funding. Unlike other FinTechs, it mainly targets lower-income people who enjoy various cashbacks. The app can match a person’s location-based searches with their in-store purchases to:
- Offer targeted discounts at specific locations.
- Add payment locations to payment checks, reducing the calls to validate charges.
- Minimize credit card fraud.
- Help parents control child spending.
Source: TechCrunch
Current has also implemented a point-based reward system for shopping at various locations. Timed promotions have, for example, led to a 5x increase in sales for a fast food franchise and a 6% increase in sales per customer for a local pharmacy.
Location Intelligence allows the company to bypass expensive attribution models used by competitors and improve its targeting. As a result, Current provides higher rewards while offering a much better experience to people living paycheck-to-paycheck.
According to the BCG survey, using Location Intelligence for a tailored experience can increase the time spent in financial apps by up 17%. Location-based verification also decreases the number of fraudulent transactions by about 30%.
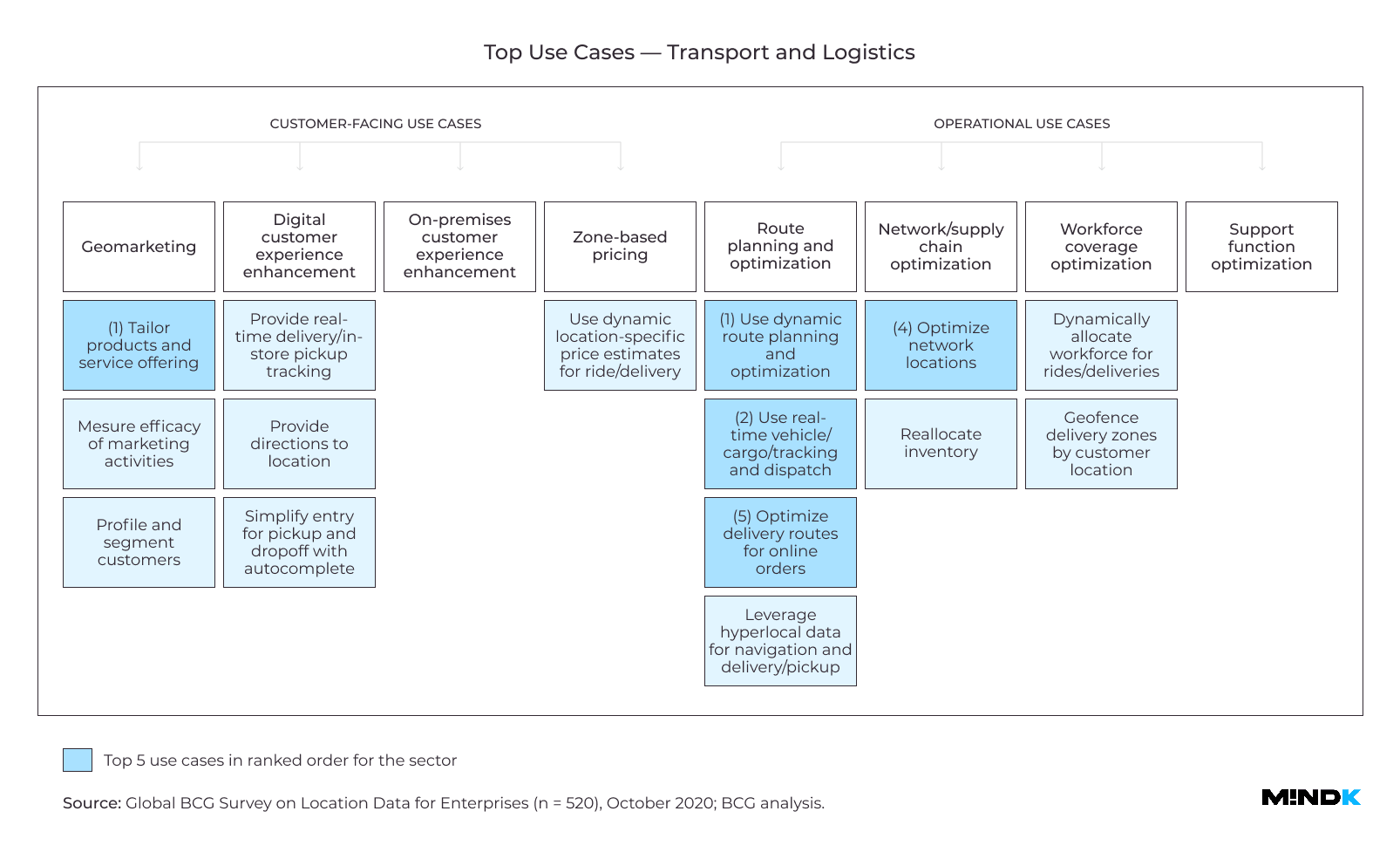
Logistics and delivery
Flaschenpost is a German startup that promises to deliver alcohol in under 2 hours. The app confirms the user’s location and provides detailed route instructions for the drivers. It can account for road hazards, traffic jams, and other factors that might impact the delivery time. Flaschenpost’s CTO Aron Spohr reveals that even the tiniest improvements in location data accuracy have a huge impact on the bottom line. Shaving 2 minutes off each roundtrip saves flaschenpost over 700 man-hours a day.
BCG survey shows LI can reduce delivery costs and improve customer satisfaction by up to 11% for logistics firms.
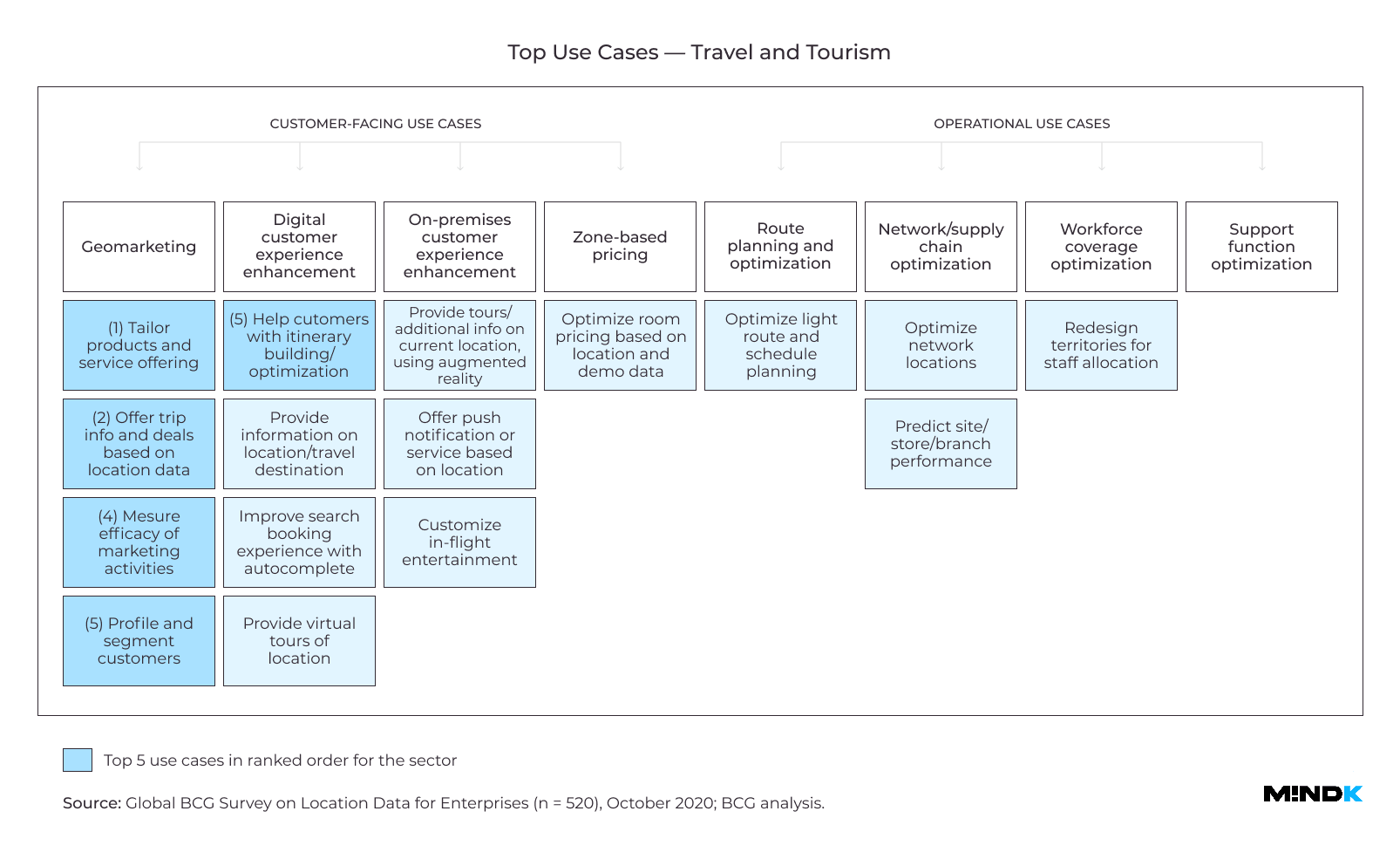
Travel industry
A leading hotel franchise from the United Kingdom was one of the first to use LI to improve the search, booking, and guest experience (GX). Soon, its competitors started offering similar features. So the company began enhancing its maps with lots of filterable information like:
- Travel options and transit times.
- Parking lots nearby.
- Local sights and cafes.
- Directions to hotel administrations and so on.
This info appeals to recreational travelers who weigh different factors when booking a trip. According to BCG study, data-rich maps achieve a 108% rise in hotel views and improve bookings by 12%.
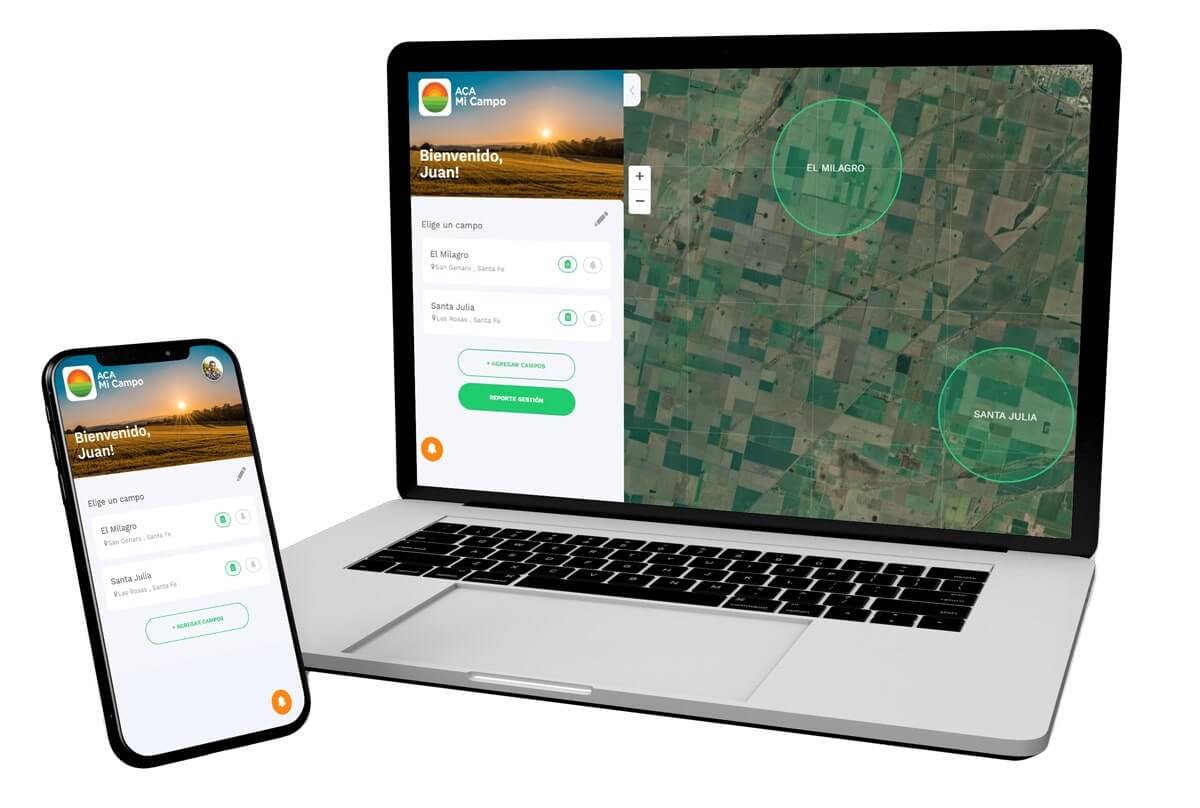
Agriculture
Argentine Cooperatives Association (ACA) has built one of the most ambitious LI systems. To help farmers monitor crops in real-time, ACA analyzes thousands of drone and satellite images with the help of AI. This allows users to detect, among other things, crop infections before they can spread to nearby areas.
The software uses geospatial, weather, and business data to help farmers make decisions in a planting season. The result is higher yields, lower expenses and environmental footprint. ACA proves that location data is an important component of digital transformation in agriculture.
Source: acacoop.com.ar
Types of geospatial data to power new business capabilities
Location data
What is it?
This type of data describes the exact position of a real-world object. It usually contains the following attributes:
- Object name.
- Coordinates (latitude and longitude).
- Postal ZIP code.
- Altitude above sea level (meters).
- Brand name and ID.
- Category name & ID.
How can you use location data?
Accurate location data forms the backbone for most of the strategies described in this article. You can use it to find optimal store locations, monitor demand nearby, track competitors, optimize local pricing, and run ad campaigns tailored to online and offline behaviors. As an example, an American food delivery service DoorDash has used this strategy to win 56% of the market share.
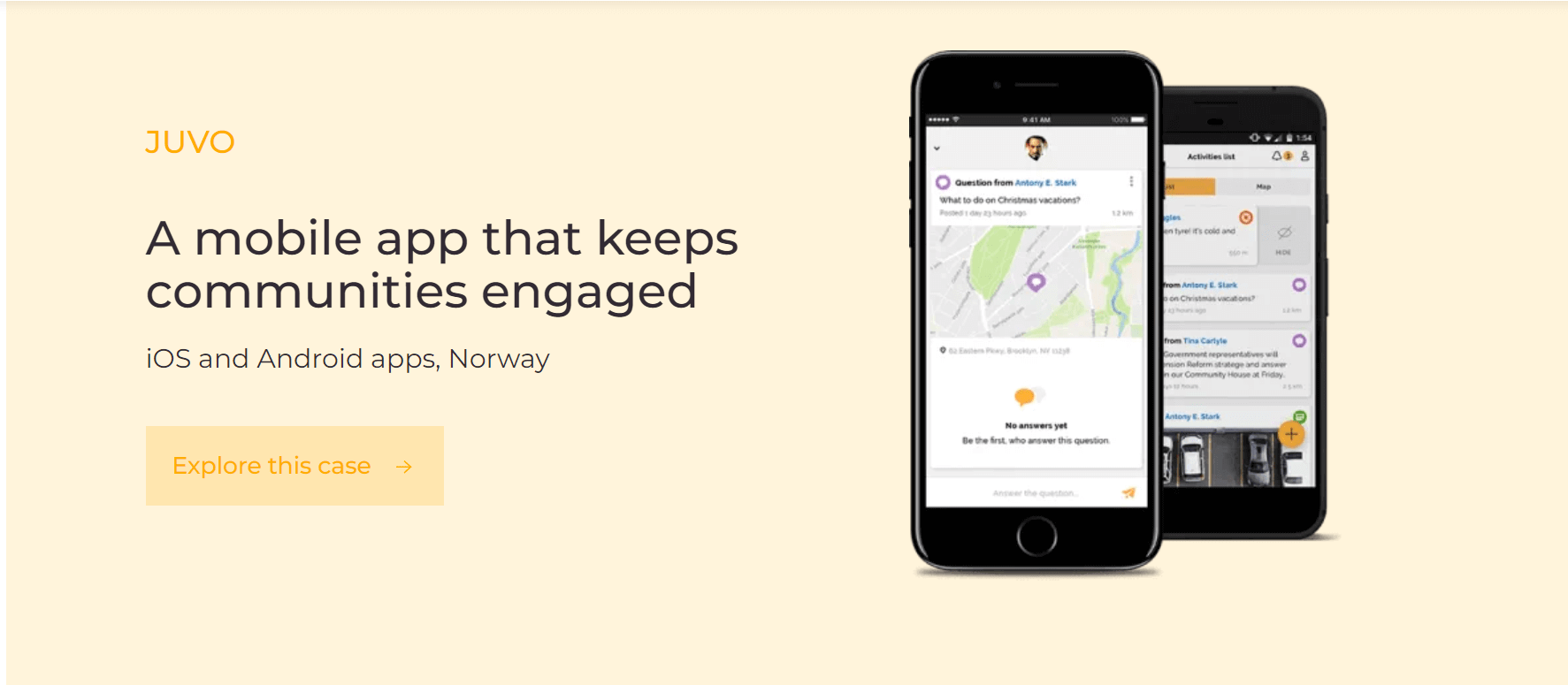
Location data is also essential for urban planning and community development. MindK, for instance, developed a location-based app for various communities in Norway. It allows business associations to organize and promote local events, manage members with the help of CRM/ERP integrations, and send location-based notifications. Some health-related groups use our app to host anonymous chat rooms and request help from members nearby. All communication is anonymized by default for secure and safe experience.
Where can you get location data?
Location data mainly comes from smartphones and other connected devices like fitness wearables and trackers in delivery vehicles. All these devices act as receivers for GPS satellites, cell towers, Bluetooth beacons, and WiFi routers.
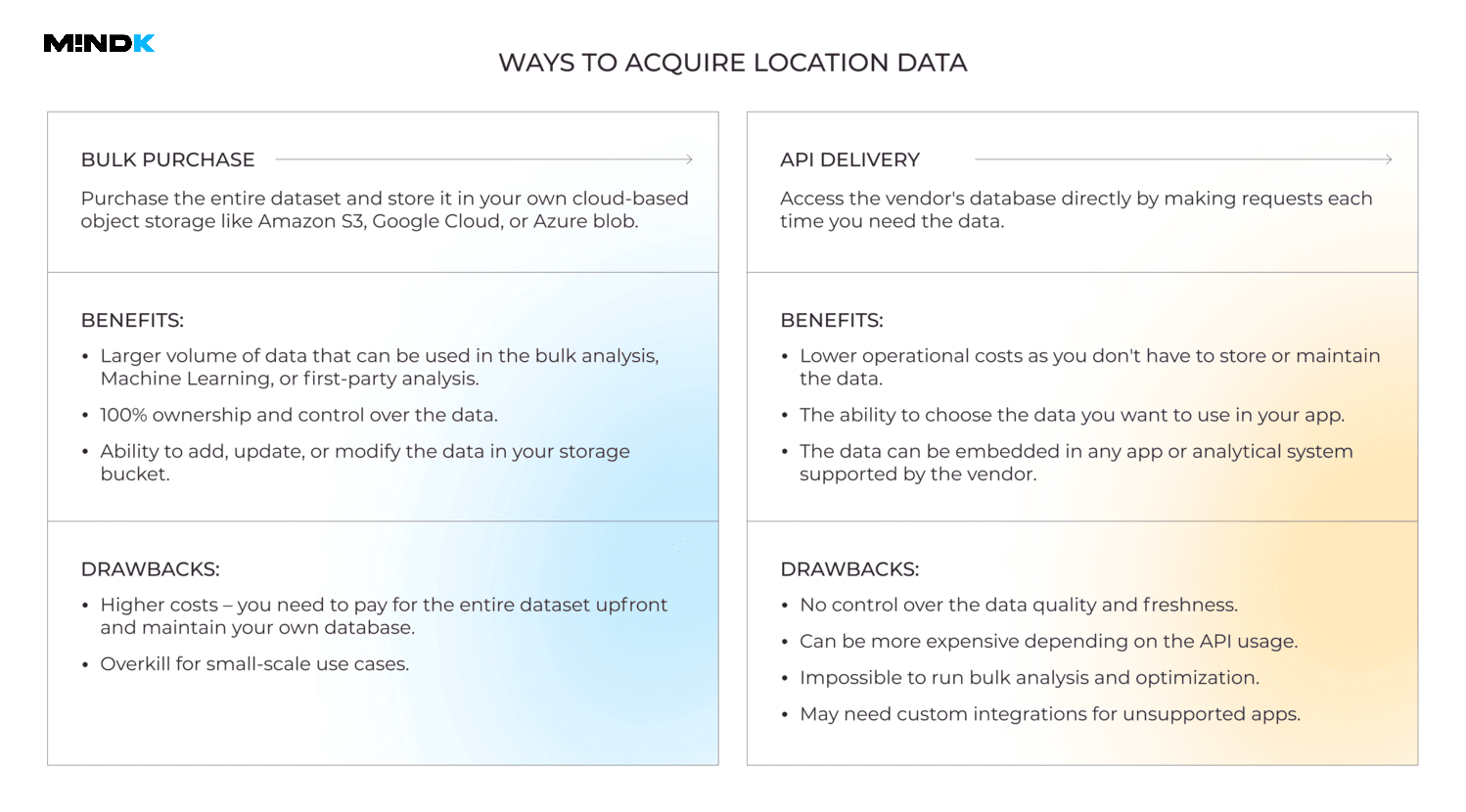
There are several ways to access data for gps tracking app development without having to collect it yourself:
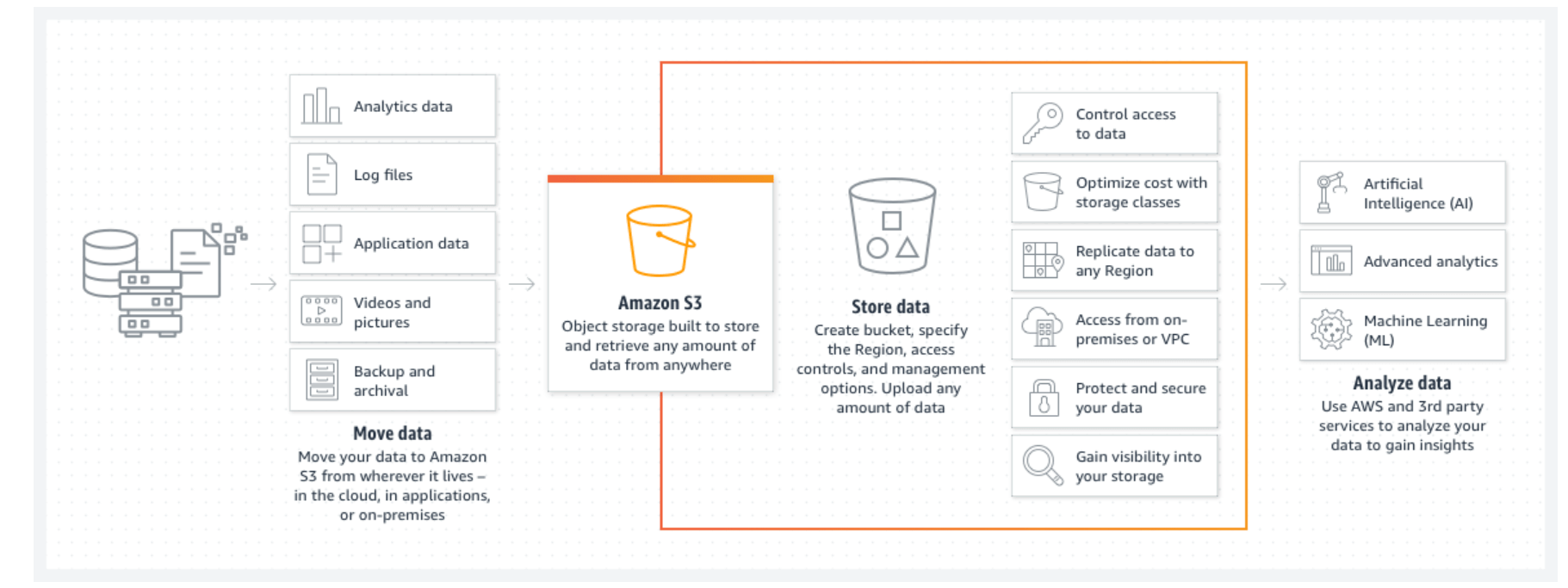
- Buy a location dataset on Amazon Data Exchange (ADX) platform. You can then move the data to your private Amazon S3 bucket – cloud-based storage for files (called objects) that can be accessed via a simple URL.
- Integrate the data using an Application Programming Interface (API). In short, API is an interface that helps integrate third-party features, exchange data, and connect systems without the need to develop them from scratch.
What are the best location data providers and APIs?
To build a geolocation app, you’ll need to use one API to learn a user’s location and another to put those coordinates on a map.
APIs for locating a mobile device:
- Google Maps API – the most popular map service in the world. It’s available for all platforms and localized into most languages. You can customize the map’s colors to fit your brand image, modify road density or remove labels from the map.
- Apple’s Core Location API –locate an iOS device, determine the direction it faces, its altitude, or the proximity to an iBeacon.
- W3C Geolocation API – a geolocation API for progressive and web applications. It’s supported by most browsers including Chrome and Safari but only works via HTTPS.
APIs for displaying a location on a map:
- Google Maps SDK – a high-quality map that shows building outlines, even in tiny villages, as well as a street view mode for major cities across the world.
- Apple MapKit – although Google’s data is generally more extensive and accurate, Apple is rapidly closing the gap. In 2020 Apple completed a rollout of a brand-new US map that boasts a much higher level of environmental detail along with a 3D view for major US cities.
- Google Maps Directions API & Google Distance Matrix API – provide directions and plan routes for public transit, cycling, walking, and driving. Determine the expected travel time depending on the chosen route, means of transportation, and traffic conditions.
Alternative sources for location data
Taking data from Google gets quite costly for high-usage apps. In map-based app development, it often makes more sense to purchase location data in bulk on platforms like ADX and Datarade:
- Lifesight Mobility/ Raw Location Data – a mobile SDK that collects anonymized location data you can get as a daily dump to a chosen URL. The database covers most of the world except for China and holds 2 years’ worth of historic data.
- Global Point-of-Interest Data – a huge location database enhanced with business and customer data on 200M+ places around the world. The dataset covers 5 years of historical data and gets daily updates.
- SafeGraph Places – location data on more than 11M places with the exception of private homes.
Foot traffic data
What is it?
This type of data, also called footfall, measures the number of visitors at cafes, hotels, or streets at different times. This data can show you how long they stay at a venue and how often they come back. You measure it with the help of WiFi and Bluetooth signals inside a building; GPS satellites outdoors; and infrared or laser sensors in a store.
How can you use foot traffic data?
All sorts of physical businesses benefit from footfall data. Some convenience stores, for example, compare foot traffic against sales to understand conversion rates, identify peak hours, optimize employee scheduling, and measure KPIs like customer retention, satisfaction, inventory turnover, and ROI.
Where can you get foot traffic data?
- Echo Analytics Foot Traffic Analysis – a huge dataset tracks foot traffic at more than 22M locations in the US and Europe. Use it to identify consumer trends, track repeated buyers, identify promising areas for business, and more.
- Bluespot AI Global Alternative Foot Traffic – a dataset that reflects changes in working hours at over 1 million locations in 240 countries. This data can serve as a proxy for customer activity.
- PREDIK Data-driven Enriched USA Foot Traffic Heat Maps – an extensive dataset that reflects foot and car traffic in the US.
Point of interest (POI) data
What is it?
POI data describes any real-world location that can be interesting to people (duh). It may be anything, from a shopping mall to a popular camping destination in the mountains. POI data typically lists the following attributes:
- Location name.
- Coordinates.
- Physical address.
- Location purpose.
- Number of visitors.
- Their behavior patterns, and so on.
How can you use POI data?
On-demand apps like Uber analyze POI data to estimate delivery times, find underserved regions and optimal routes. Logistics companies use it to optimize last-mile delivery and find optimal pickup/delivery places. Governments can improve public transit, emergency services, healthcare, and disaster response planning.
What are the best POI data providers and APIs?
- Factual Global Places keeps records on more than 130M points of interest in over 50 countries. The dataset includes over 25 attributes like address, geocode, emails, and other business information.
- Foursquare Places offers POI data on over 100M places all over the world. Its dataset includes 30+ attributes you can use to enrich your strategic planning and mapping services. The company pays great efforts to keep this data fresh, accurate, and consistent.
- Tamoko provides POI data on more than 200M places as a part of its location as a service (LaaS) offer. The company uses a proprietary SDK and Machine Learning algorithms to ensure the data is accurate, transparent, complete, and GDPR-friendly.
Map data
What is it?
Map data helps create all sorts of interactive maps, from weather forecasts to live traffic updates. It typically has multiple sources and layers. Street photos, videos, land surveys, GPS data, and satellite imagery can all form your primary layer. You can then add a secondary layer – demographical, consumer, or climate data – to derive actionable insights.
How can you use map data?
Map data is vital for lots of industries. Police stations can, for example, map various districts by crime rates and types when prioritizing attention and creating patrol routes. Real estate companies like Nomoco use map data to select optimal locations for construction sites and identify lucrative investment opportunities. And automakers, like BMW, use map data to improve driving safety.
What are the best map data providers and APIs?
- MBI Geodata HERE Map Rendering – detailed 2D maps of roads, structures, and places in 230 countries across the world with 5M+ daily updates. The company offers pay-as-you-go and annual subscriptions for a variety of features.
- Matrixian Map – customizable interactive maps that combine various types of location data, including real estate, logistics, business, point of interest, and demographics. The dataset covers most countries over the globe and gets daily updates.
- csv2geo – a solution that simplifies geocoding, converting physical coordinates into postal codes and back. The service is available in the form of API requests and text/file uploads.
Satellite data
What is it?
This type of data comes from satellite images that use high-resolution cameras, thermal sensors, laser, and radar reflections. As a rule, satellite data has the following attributes:
- Geometric resolution – how much land is stored in a single pixel of the image.
- Radiometric resolution – the level of brightness and contrast.
- Temporal resolution – the time an image was taken.
- Spectral resolution – the time between wavelengths and their frequency.
- Spatial resolution – the existence of different objects on an image.
How can you use satellite data?
Satellite data allows scientists to get insights into natural disasters and ecosystems, helps governments prepare for emergencies, and assists companies in developing new business opportunities. Its main benefit is the sheer amount of data available for analysis and predictions.
What are the best satellite data providers and APIs?
- Sky Watch EarthCache – a cloud-based platform for one of the world’s biggest networks of satellite image providers. Its powerful API gives you everything you need to develop business applications on top of satellite data.
- CustomWeather Satellite Imagery & Data – global infrared satellite imagery in a 10km/pixel resolution with hourly updates. The service is available as a REST API with monthly and annual billing.
- Aviation Edge Satellite Tracker API – real-time tracking of satellites and other objects orbiting the Earth (including their name, launch date, and orbital position).
How to build a location-tracking app: the cloud-native approach
Modern consumers expect fast innovation and excellent services. The problem is that traditional monolithic applications are extremely unwieldy. Even if you need to scale the tiniest part of your solution, you’ll have to scale the entire server. The same goes for deploying new functionality.
A cloud-native approach emerged as a way to address these challenges cost-effectively. Cloud-native apps leverage the capabilities of next-gen cloud platforms like Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud. A great variety of architectural approaches has good synergy with these platforms. Domain-driven design,microservice, serverless, and event-driven architecture, you name it.
These approaches can provide numerous benefits like easier scaling and ease of deployment.
Take, for example, the microservice architecture. It splits large applications into small independent modules. Each of these so-called microservice fulfills a single business function and talks to other services via an API. This gives you the flexibility to deploy new changes without affecting other services. You can package microservices in isolated containers with tools like Kubernetes. This allows you to scale services on-demand and release changes with almost no downtime.
Or you could choose the serverless approach I currently use on my real estate project. It delegates most of the routine tasks to the cloud provider. So you don’t have to provision the infrastructure, manage availability, and even deploy the app. Developers write less code, which means fewer bugs. The cloud takes care of autoscaling and fault tolerance.
What’s more, such platforms have an incredibly flexible billing system. You choose the features you need and only pay for the computing resources you actually use. For one of our clients, this approach saved $14K per month on infrastructure costs alone.
Conclusion
Location Intelligence provides a huge opportunity for businesses in all niches. The latest advances in cloud computing, analytics, and data exchange platforms make geolocation app development more accessible than ever.
At MindK, we recommend using the cloud-native approach for most of our new clients. Such applications are inherently more scalable, resilient, easy to monitor, and update without disrupting the user experience.
So, if you’re interested in location-based app development, don’t hesitate to drop us a line. We know how to implement it in a cost-effective fashion.